====(NoProfile) Prevents from loading profile scripts====
-nop
-NoP
-noprofile
-NoProfile
-noP
====(NonInteractive) Prevent create prompt====
-noni
-NonI
-noninteractive
-NonInteractive
-nonI
====(WindowStyle Hidden) Prevent Windows Display====
-window hidden
-W Hidden
-w hidden
-windowstyle hidden
-win hidden
-WindowStyle Hidden
-win Hidden
-wind hidden
-WindowStyle hidden
-WindowStyle hiddeN
-windows hidden
-Win Hidden
-win hid
-Window hidden
-Wind Hidden
-Win hidden
====(EncodedCommand) Decode base64 encoded strings====
-enc
-Enc
-EncodedCommand
-encodedcommand
-encodedCommand
-ec
-en
-ENC
====Execution Policy Bypass====
-ep bypass
-exec bypass
-executionpolicy bypass
-Exec Bypass
-ExecutionPolicy ByPass
-ExecutionPolicy bypass
-Exec ByPass
-ExecutionPolicy Bypass
-ExecuTionPolicy ByPasS
-exe byPass
-ep Bypass
-ExecutionPolicy BypasS
-Exe ByPass
====(NoLogo) Hides the copyright banner====
-Nol
-NoL
-nologo
-nol
Tools that could help during static and dynamic analysis:
- Windows PowerShell ISE
- Debugger for PowerShell script
- Wireshark
- Capture network traffic
- Sysmon
- Advanced system monitor tool
- Sysmon Configuration File (using SwiftOnSecurity)
- Configuration file for Sysmon
- Process Monitor
- Capture details running processes
- Windows Event Logs
- Event logs for Windows
Static Analysis
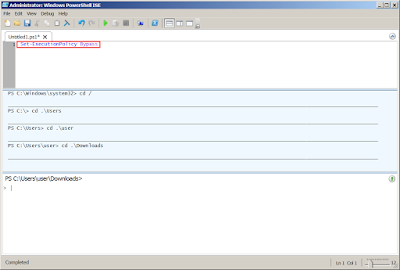
Malicious Powershell script at Notepad++:Open Powershell ISE:
Start > Type "powershell" > Right click Windows PowerShell ISE > Run as Administrator
*Note* Need to set Set-ExecutionPolicy Bypass
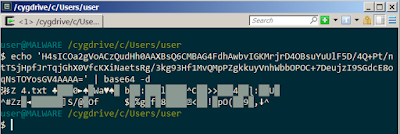
Copy the highlighted base64 encoded strings and perform decoding:
It is binary file. Refer back to the PowerShell , notice that it is compressed by GZIP.
Let PowerShell ISE decode the base64 strings and decompress the GZIP for us.
Edit the PowerShell and paste it into PowerShell ISE as below. (There is two quotes '' change it to single quote ')
Write the decoded and decompressed malicious script into a text file using Write-Output then hit F5 to Run.
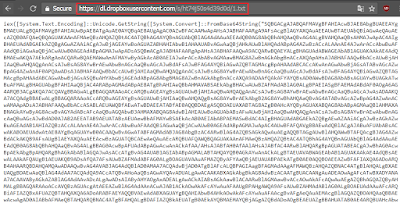
Below is the malicious script will download a text file from Dropbox and
Open the Dropbox content at Browser. Notice that it is another malicious script with base64 encoded.
Copy the encoded strings then decode it at ConEMU. Notice it connects back to malicious C2 server. It is malicious script generated by Empire.
Dynamic Analysis
Open Windows PowerShell ISE.
The malicious PowerShell script.
Open Wireshark.
Run CMD as Administrator.
Install Sysmon Configuration File.
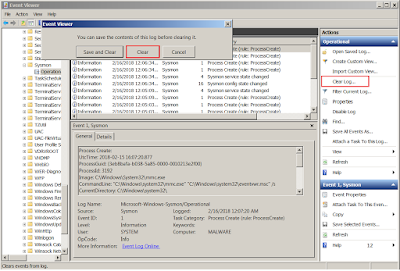
Open Windows Event Viewer.
Notice the Sysmon in Event Viewer.
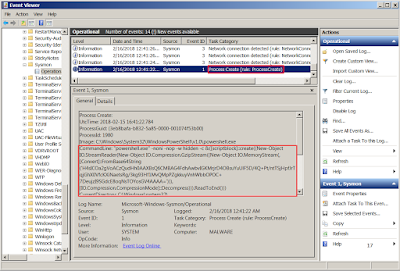
Copy the PowerShell script in purple highlighted into PowerShell ISE.
Start capture the network traffic in Wireshark.
Clear Sysmon Event Logs.
Run the PowerShell ISE by hitting F5.
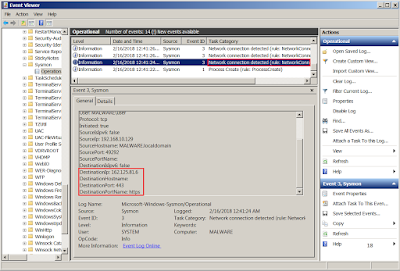
Notice the network traffic in Wireshark contain Dropbox and C2 server.
Notice the logs captured in Sysmon contain PowerShell process and network connection.
Save the Wireshark traffic and Sysmon Logs then revert the virtual machine.
End of Just another Malware Analysis Guide (4) - Fileless Malware (PowerShell)
























No comments:
Post a Comment